Introduction to Semiconductors
WHAT IS A SEMICONDUCTOR?
Materials whose conductivity lies between those of conductors and insulators are called semiconductors.
The most commonly used semiconductors are germanium(Ge) and silicon(Si).
(google images)
CONDUCTION OF SEMICONDUCTORS
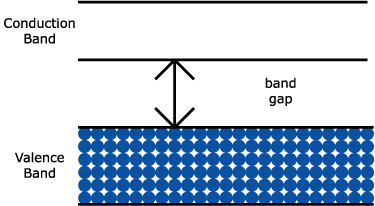
The conductivity and resistivity of materials depends mainly on the energy gap between conduction band and valence band.
(google images)
For conductors there is no electron gap and hence conduction band and valence band overlap each other.
If large potential difference is applied across the valence band, then electrons jump into conduction band and hence conduct electrons.
For silicon and germanium 1.1eV and 0.71eV needs to be applied for electrons to jump into the conduction band.
Charges in valence band are under nucleus influence. Generally charges in the conduction band are the ones which move.
PROPERTIES OF SEMICONDUCTORS
Semiconductors have crystalline structure and are tetravalent.They form four pairs of covalent bonds with their neighbours.
At low temperature electrons are rigidly held in the bonds and conductivity is less, but as the temperature increases some covalent bonds are broken and electrons become free and as a result conductivity increases
.
(google images)
CLASSIFICATION OF SEMICONDUCTORS
Semiconductors are usually in elemental form or compound form.
Elemental semiconductors: germanium, silicon
Compound semiconductors:
Inorganic: CdS,GaAs
Organic: Anthracene
There 2 types of semiconductors:
1.Intrinsic semiconductors
Semiconductors in their purest forms are called intrinsic conductors.The electrical conductivity in intrinsic semiconductors is due to free electrons and holes.
n(i) = n(e) + n(h)
If a potential is applied across an intrinsic semiconductor then current I = I(e) + I(h).
example: silicon,germanium
2.Extrinsic semiconductors
Semiconductors which are doped by various other compounds or impurities are called as extrinsic semiconductors.
Semiconductors are usually doped to bring changes in their electrical conductivity and form p-type and n-type semiconductors.
- P-type semiconductor
P-type semiconductors are formed by adding trivalent(acceptor impurity) elements like aluminium,indium or gallium to an intrinsic semiconductor. Due to this , there are more number of holes and hence major carriers are holes n(h)>>n(e).
(google images)
- N-type semiconductor

(google images)
N-type semiconductors are formed by adding pentavalent (donor impurity) elements like phosphorous, antimony to an intrinsic semiconductor. Due to this , there are more number of electrons and hence major carriers are electrons n(e)>>n(h).
- P-type semiconductor
(google images)